
Steering systems are critical to vehicle control and manoeuvrability. They are in charge of allowing the driver to alter the direction of the vehicle, ensuring safe and efficient road navigation. Steering systems have changed over time, with many versions available to accommodate diverse vehicle designs and driver preferences. In this topic, we will look at the types of steering systems.

A steering system is a mechanical or electronic system that enables the driver to control the direction of a vehicle. It connects the driver’s input from the steering wheel to the wheels, allowing for precise steering control. The primary function of a steering system is to translate the driver’s steering inputs into corresponding wheel movements, resulting in a change in the vehicle’s direction.
The importance of steering systems lies in their contribution to vehicle safety and manoeuvrability. A well-functioning steering system ensures that the driver can navigate turns, curves, and obstacles on the road with ease and precision. It allows for quick response and control, enhancing the driver’s ability to avoid accidents and maintain stability. A reliable steering system is vital for maintaining proper vehicle alignment, tyre wear, and overall road handling performance.
There are main 2 types of steering systems:
The manual steering system, as the name suggests, requires direct physical effort from the driver to turn the wheels. It utilizes mechanical linkages and a steering gearbox to transmit the driver’s input to the wheels.
The components of a manual steering system typically include a steering wheel, steering column, steering gearbox, pitman arm, center link, and tie rods. When the driver turns the steering wheel, the steering column transfers the rotational motion to the steering gearbox. The gearbox then converts the rotational motion into linear motion, which is transmitted to the wheels via the pitman arm, center link, and tie rods.
4 types of manual steering systems
 and pinion steering" width="563" height="317" />
and pinion steering" width="563" height="317" />
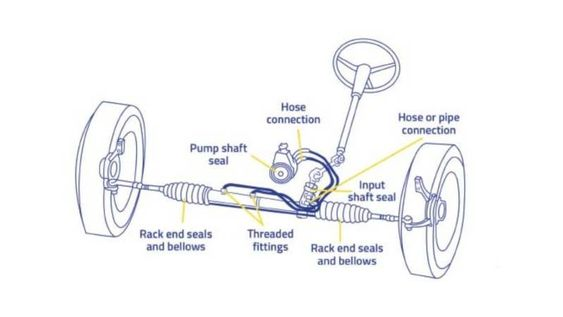
Rack and pinion steering is a popular and widely used type of steering system in modern vehicles. It offers a straightforward and efficient mechanism for converting the rotational motion of the steering wheel into the linear motion required for steering the wheels.
In a rack and pinion steering system, the main components include a rack, a pinion gear, and tie rods. The rack is a long, toothed metal bar that is connected to the steering wheel via the steering column. The pinion gear, which is a small round gear, meshes with the teeth on the rack.
When the driver turns the steering wheel, the rotational motion is transferred to the pinion gear. As the pinion gear rotates, it moves the rack either to the left or right. This linear movement of the rack is then transmitted to the tie rods, which are connected to the steering knuckles and control the movement of the wheels. The tie rods push or pull the wheels, causing them to turn in the desired direction.

This steering mechanism, sometimes referred to as the worm and sector or the recirculating ball and nut, is typically seen in ancient cars and large trucks. The way it operates differs from a rack and pinion. Before we discuss the task, let’s have a look at how the recirculating ball steering system is built.
The worm gear and the sector gear are the two gears that make up the recirculating ball steering system. A threaded shaft is attached to a block and the steering wheel. The block is threaded in such a way that the worm gear may pass through since the worm gear is relatively large. The sector gear is attached to the gear teeth on the exterior of this block. The pitman’s arm is then linked to this sector gear, and the pitman’s arm is finally connected to the tie rod. The worm gear’s thread is filled with ball bearings inside the block. The mechanism works similarly to a rack and pinion.
The steering shaft rotates together with the steering wheel as it is turned. The gear is fastened to prevent up-and-down movement. This causes the worm gear and the block to revolve. The block moves as a result of the rotation since nothing is holding it in place. Following that, the sector gear and the pitman’s arm are both moved by the moving block. Ball bearings are inserted into the worm gear’s thread to lower friction and avoid gear slippage.

The worm and sector steering system is an older type of manual steering system that is still used in some vehicles today. It consists of a worm gear and a sector gear. When the driver turns the steering wheel, the worm gear rotates, causing the sector gear to move. This motion is then transmitted to the pitman arm and the tie rods, resulting in the turning of the wheels.
One of the advantages of the worm and sector steering system is its simplicity, which makes it less expensive to manufacture and maintain. However, it is not as precise or efficient as other steering systems, and it may have more play in the steering mechanism. Worm and sector steering systems are commonly found in classic cars and some older models.
The cam and roller steering system is a less common type of manual steering system. It consists of a camshaft and roller followers. When the driver turns the steering wheel, the camshaft rotates, causing the roller followers to move. This motion is then transmitted to the tie rods, which turn the wheels.
One of the advantages of the cam and roller steering system is its smooth operation, providing a comfortable driving experience. It also requires less physical effort from the driver compared to other manual steering systems. However, it is more complex and may be more prone to wear and tear. Cam and roller steering systems are not as widely used as the previously mentioned types.
Power steering is an essential component in modern vehicles, greatly enhancing the ease of steering and overall driving experience. It utilizes different systems to assist the driver in maneuvering the vehicle with minimal effort.
Power steering is a mechanism that assists the driver in turning the wheels of a vehicle. It reduces the effort required to steer, making it easier to control the vehicle, especially at low speeds and during parking. There are different types of power steering systems available, each with its working principle and advantages.
Types of power steering systems:

Hydraulic power steering is a type of power steering system that uses hydraulic pressure to assist the driver in turning the wheels.
Hydraulic power steering (HPS) systems are widely employed in automobiles to assist drivers in maneuvering their vehicles with ease. These systems utilize hydraulic pressure to reduce the effort required for steering, especially during low-speed manoeuvres and parking.
At the core of a hydraulic power steering system lies the power steering fluid. This specialized fluid plays a crucial role in transmitting force within the system. It acts as a medium for transferring hydraulic pressure from the steering pump to the steering gearbox, thus assisting in turning the wheels.
A typical hydraulic steering system consists of several key components. The steering pump, driven by the engine, generates hydraulic pressure. The power steering fluid is stored in a reservoir, ensuring an adequate supply for the system. From the pump, the pressurized fluid flows to the steering gearbox. Here, the fluid’s hydraulic force is converted into mechanical force, enabling the wheels to turn. The steering linkage and tie rods connect the steering gearbox to the wheels, translating the steering input into physical movement.
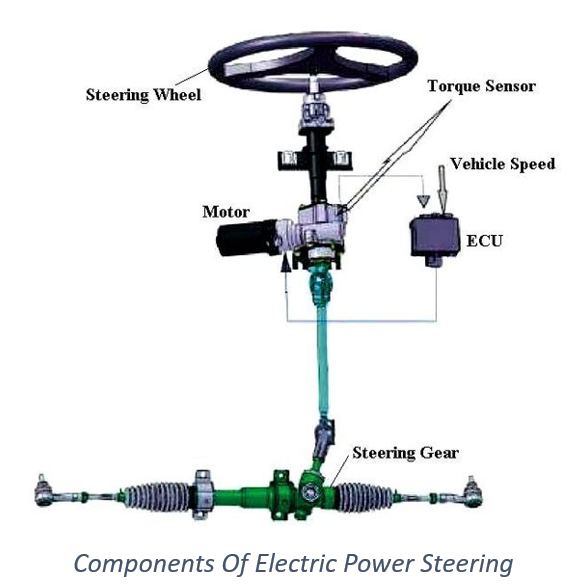
Electric power steering (EPS) has revolutionized the automotive industry by replacing traditional hydraulic power steering with an efficient and advanced system.
The electric power steering system is a technology that assists the driver in turning the vehicle’s wheels effortlessly, providing a smoother and more responsive driving experience. Unlike hydraulic power steering, which relies on hydraulic pressure generated by the engine, electric power steering employs an electric motor to assist with steering manoeuvres.
In an electric power steering system, the ECU continuously monitors inputs such as steering wheel angle, vehicle speed, and torque applied. Based on this information, the ECU calculates the appropriate level of assistive torque and sends a command to the electric motor. The motor then applies the necessary force to the steering column, assisting the driver’s steering effort.

Electro-hydraulic power steering (EHPS) combines elements of both hydraulic and electric power steering systems. It utilizes hydraulic pressure from a pump driven by an electric motor to provide steering assistance.
The working principle of electro-hydraulic power steering is a combination of hydraulic and electric systems. The electric motor drives the power steering pump to generate hydraulic pressure. The control valve directs the pressurized hydraulic fluid to assist the steering motion. The amount of assistance is determined by the driver’s input and the vehicle’s operating conditions, similar to hydraulic power steering.
Steering systems are a vital component of any vehicle, ensuring precise control and manoeuvrability. In this article, we explored types of steering systems: rack and pinion, recirculating ball, warm and sector, cam and roller, hydraulic power steering, electric power steering and Electro-hydraulic power steering. Each system has its own set of advantages and disadvantages, catering to different vehicle types and driving preferences. By understanding the inner workings of these systems, we can appreciate the engineering behind smooth and responsive steering.
For a small car, a rack and pinion steering system would be a suitable choice due to its compactness and responsiveness.
Yes, electric power steering systems are generally more fuel-efficient compared to hydraulic systems, as they eliminate the need for a hydraulic pump.
It is possible to upgrade a vehicle’s steering system, but it can be a complex and expensive process. Consult with a professional mechanic to determine the feasibility and cost.
Electric power steering systems require minimal maintenance compared to manual steering systems. However, it is recommended to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for regular inspections.
One potential drawback of electric power steering is the loss of power assistance in case of electrical system failure, which can make steering more challenging.